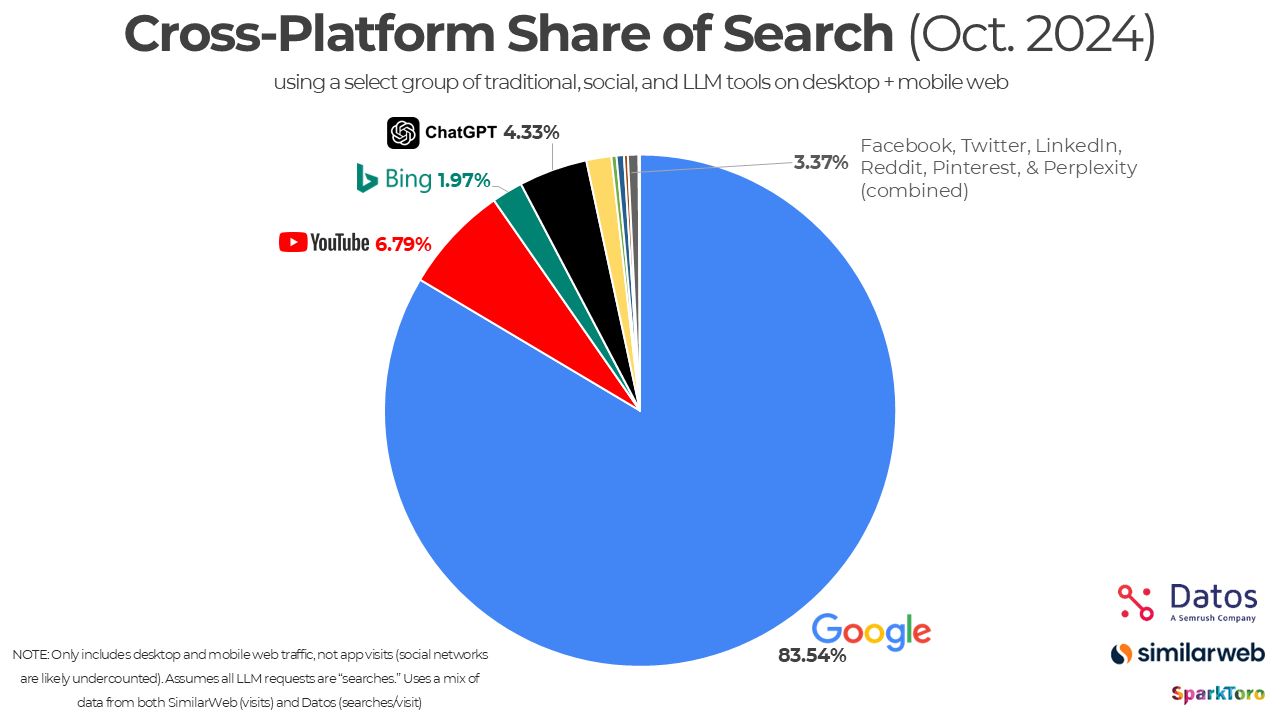
GEO: 5 powerful tips to boost your visibility with LLMs
Good news: adapting to GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) doesn’t require relearning everything from scratch. It’s mainly about extending your solid SEO practices and developing new reflexes centered on structuring information and ensuring reliability. Here are the concrete areas to focus on to align your strategy with GEO requirements.
1. Create content designed for both AI and users
The question often arises: “Should we now write to please AI or to please humans?” The answer is simple: both at the same time. Fortunately, what’s good for the user (clarity, relevance) is also good for AI. In practice, revisit your key content with a fresh eye: if a paragraph were extracted on its own, would it still make complete sense? Does each section deliver a well-defined key idea?
-
One idea per paragraph: structure your text so that each paragraph conveys a single main idea. This creates clear units of meaning that AI can extract without requiring the full context. For example, avoid long, sprawling paragraphs that mix several concepts.
-
Explicit headings for each section: use subheadings (H2, H3, etc.) that clearly describe the content of the section that follows. These subheadings act as signposts for both your readers and the algorithm. A well-crafted heading helps AI understand, “Ah, this section is about the advantages of this solution,” and extract it accordingly.
-
Clear and natural language: avoid excessive jargon or convoluted phrasing. Prefer short, precise sentences, as if you were explaining to a smart beginner. An AI (just like a busy human reader) doesn’t have time to decipher complicated sentences. Tip: why not use tools (e.g., Hemingway or others) to flag overly long or confusing sentences in your drafts? This helps you simplify without dumbing down. In fact, shortening and clarifying your sentences makes life easier for AI.
-
Comprehensive coverage and expertise: GEO-friendly content is, above all, quality content. Keep covering your topics in depth, adding real value. An article that tackles a subject thoroughly and expertly has a greater chance of becoming the reference that AI cites. Don’t hesitate to include expert contributions, concrete examples, or case studies—these reinforce your content’s E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness). Show that you master your topic better than anyone else.
In short: keep producing excellent content as you would for SEO, but with greater emphasis on readability and precision.
2. Structure your pages to be “scannable” by AI
Structure is the backbone of GEO. Think of AI as a super-reader that skims your pages to extract the essentials without reading every single word. Make its job as easy as possible.
-
Leverage lists and easy-to-extract formats: generative answers often present information in bullet points, numbered steps, or comparison tables for clarity. If your content already contains these well-structured formats, you increase the chances of having parts reused as-is. For example, a well-crafted FAQ with a clearly posed question and a concise answer has a high chance of being picked up by AI to respond to the same query. Likewise, a clear comparison table (e.g., a “SEO vs GEO” table with columns) is ready-made for an AI wanting to explain differences. The same goes for standalone definitions (“Machine learning is…”) that a model can cite directly when someone asks for a definition. Pro tip: at the end of your sections or articles, include a short bullet-point summary of the key ideas—these recaps are a goldmine for generative models.
-
Use semantic HTML tags: make sure to use heading tags (H1, H2, H3, etc.) and list tags (
<ul>,<ol>for bullets/numbers,<dl>for definition lists, etc.) properly in your HTML code. A well-formed hierarchy not only helps human readers navigate but also allows AI to better segment and contextualize each part. On the flip side, avoid a jumble of<div>without structure or headings out of order—that can confuse the algorithm. In practice: one<h2>per major section,<h3>for subsections, and if possible, use<section>or<article>elements in your code to clearly delimit logical content blocks. Each “chunk” of your page should be understandable on its own, and structure helps achieve that. -
Keep paragraphs short and focused: as mentioned earlier, avoid overwhelming walls of text. Aim for 2–4 sentences per paragraph. A short paragraph should capture one clear unit of meaning that’s easy for AI to digest. Bonus: this also makes your content more pleasant for human readers.
-
Use visual snippets: whenever possible, enrich your pages with informative visuals—infographics, diagrams, images with explanatory captions. This not only engages human readers but also helps AI, which can pick up on captions and alt text to extract information. For example, a chart with a caption describing a key statistic can be referenced by AI (since generative engines also read captions and alt text).
In short: think UX + structure. What’s skimmable for a human is equally skimmable for AI. Well-structured content is “attractive” content for generative engines. And the good news? It’s exactly the same best practice we’ve been advocating for impatient internet users for years!
3. Focus on reliability: sources, citations, and updates
Trust is the new gold standard in GEO. Remember: an AI doesn’t “verify” the absolute truth of what you write, but it relies on content it deems trustworthy to build its answers. To earn that trust, your content must radiate credibility.
Here are some levers to activate:
-
Cite your sources explicitly: don’t just write “According to a recent study…” without further detail. Instead, say “According to a 2023 study by INSEE…”. Provide the author or organization, the date, and even the publication if relevant. Why? Because AI will recognize that the information is backed by a reliable source rather than a vague claim. By citing properly, you strengthen your informational legitimacy while giving AI useful context to assess credibility. Think about it: citing also means being read (by the machine). Content with clear references will be perceived as more trustworthy.
-
Include concrete data and figures: quantitative claims, statistics, and precise facts reinforce credibility. On top of that, these elements can be directly reused by AI in its answers. Example: “85% of consumers… (Source: Study X).” Sentences like this are highly likely to show up in a generated response to support a point—and you’ll be cited as the reference. One study even showed that including relevant data points can significantly increase content visibility in AI responses (up to +40%).
-
Keep your strategic content updated: AIs favor fresh and relevant information. While a model like GPT-4 may have a fixed knowledge cutoff, many generative engines (Bing, Google SGE, etc.) rely on real-time web data. Outdated content has less chance of being reused—or worse, it could cause the AI to spread inaccuracies. Identify your key pages (those that generate leads or answer common questions) and keep them fresh: updated numbers, recent examples, mentions of the latest trends. This ensures that when AI “picks up” your content, it finds valid, timely information. Google already values freshness in traditional SEO, and it’s very likely that AIs also prefer up-to-date content—especially for things like technology advice or market data.
By strengthening the reliability of your content, you win on two fronts: human readers will trust you, and AIs will view you as a credible source worth citing. Remember: in the AI ecosystem, perceived truth often prevails—and that perception largely comes from the quality of your sources and the seriousness of your writing.
4. Optimize the technical side: your site must be readable by AI
You can have the best content in the world, but if it isn’t technically accessible to search engines (classic or AI), it won’t matter. Technical optimization for GEO largely builds on the basics of technical SEO, with a few extra points to pay close attention to.
-
Ensure your pages are indexable by bots: this may sound obvious, but check that you haven’t accidentally blocked AI crawlers. They generally follow the same
robots.txtrules as other bots. So, avoid inappropriate disallows. If, for some reason, you want to prevent your content from being used by AI (some companies do this for protected material), you can block them viarobots.txt. But if your goal is maximum visibility, open the gates. In practice: nonoindextags on your key pages, no unnecessary restrictions for user-agents, etc. A page that isn’t crawled has zero chance of being cited. -
Watch out for JavaScript-heavy content: this is a technical but crucial point. Current generative engines aren’t as good as Google at processing dynamically generated JavaScript content. Google has its rendering service (Google WRS) that executes JS to index what appears after page load. Most AIs don’t (yet) have such a full rendering service. As a result, if your site displays text only after a script runs (for example, client-side API-loaded content, or a 100% React app without SSR), the AI may see nothing at all. Make sure your essential content is present in the initial HTML or loads very quickly. If necessary, implement Server-Side Rendering (SSR) or dynamic rendering for important public pages, so even a basic crawler can access the content immediately. This is already a good SEO practice—and it’s even more important for GEO.
-
Optimize loading speed: a page that takes too long to load or requires 50 third-party scripts is bad for both users and bots. While there’s no formal proof that AIs prefer faster pages, it’s very likely (they aim to deliver quick answers “at record speed”). So, improve your Core Web Vitals scores, compress images, and remove unnecessary scripts. Provide fast access to information. At the very least, even if it doesn’t directly help the AI, your human visitors will thank you—and Google already takes that into account.
-
Leverage structured data (Schema): structured data (Schema.org) is a language used to “talk” to search engines. Google has been using it for years to deliver rich results. It’s highly likely that generative engines also rely on this markup to better understand elements like products, FAQs, reviews, etc. So keep integrating (or start integrating) relevant Schema markup on your key pages. Examples: FAQ schema on FAQ pages (to explicitly mark questions and answers), HowTo schema for tutorials, Product schema on product pages with attributes, etc. This markup isn’t visible on screen, but it provides extra context to bots about your page content. If it already helps get rich snippets on Google, it may well help tomorrow with rich answers in AI.
In summary: your technical foundation must be solid—a well-built, fast, easily crawlable, and parsable site. This is a prerequisite for SEO and just as crucial for GEO. What AI cannot see, it cannot cite—always keep that in mind.
5. Grow your “web footprint” and authority beyond your site
The last pillar of GEO—and by no means the least: to be the answer, you first need to be on the AI’s radar. A conversational AI doesn’t rely only on your official website. It learns and draws knowledge from a wide range of sources: Wikipedia, forums, online media, niche blogs, social networks, and more. If your name or content appears “nowhere” outside of your site, your chances of being cited by AI drop dramatically. That’s why it’s crucial to build your broader online presence—your digital footprint.
Here are a few ways to get there:
-
Contribute on other influential platforms: think about guest blogging on websites in your field, writing opinion pieces or guides for online media, publishing on LinkedIn if that’s where your industry is active, or answering questions on Quora/Reddit. The goal is to multiply the occasions where your expertise is visible outside your own site. Not so much for the backlink (though that can bring traffic), but so that your name or brand is regularly cited in relevant contexts. AIs pick up on these weak signals: if your company is frequently mentioned on a given topic, across different sources, they’ll identify you as part of the landscape on that subject.
-
Get mentioned in reliable sources: ideally, aim to be cited in studies, reports, interviews, podcasts, or conferences. If a government site or a reference report mentions your work, that’s powerful. But even short of that, being cited in industry newsletters, content aggregators, or articles by influencers in your niche contributes to your legitimacy. Traditional link-building sought backlinks; GEO values mentions themselves, even without links. The goal is to make your entity (person or brand) exist within the wider informational ecosystem.
-
Engage in communities: on specialized forums, Reddit, Stack Overflow (if relevant), or social networks, join the discussions in your field. By helping users and sharing valuable insights, you create content outside your site that models can ingest. For example, a detailed answer you post on a technical forum—even if it doesn’t bring direct leads—might one day serve as a source for an AI. At the same time, it reinforces your expert image among humans, often leading to more natural mentions of your name (a snowball effect for visibility).
-
Monitor your online reputation: keep an ear out for what’s being said about you. If misinformation circulates, correct it. For instance, an inaccurate Wikipedia article about your company, or a forum where someone shares outdated information about your services. Since AIs can repeat things they’ve read here or there, you’ll want to prevent errors from spreading. A concrete example: if ChatGPT incorrectly states that your product lacks a feature it actually has, it might be because of an old blog comment saying so; correct the source if possible.
By strengthening your presence beyond your site, you anchor your brand in the “memory” of the web. This way, AIs will have more material to draw from when answering questions in your domain. It’s long-term work that aligns with the principles of content marketing and personal branding—but in the GEO era, it takes on an even more strategic dimension.
Opportunities offered by GEO to boost your leads and competitiveness
Adopting GEO isn’t just about defensive prevention in the face of change—it’s also about seizing new growth opportunities for your business.
The first obvious opportunity: gaining visibility where your competitors aren’t yet present. If you start optimizing your content for AI now, you can occupy the space and become the go-to reference models prefer to cite. Being an early adopter of GEO gives you a lasting advantage, because once AI “gets used to” including you as a trusted source, it will be hard for a newcomer to take that spot. It’s a bit like being the first to rank on an SEO keyword 10 years ago—you benefit from a long head start.
Next, GEO can help you improve lead quality. As mentioned earlier, prospects coming through AI recommendations often arrive with stronger trust and clearer intent. They’ve asked the AI for advice or a product, and your offer was suggested—immediately placing you at the top of their list. The conversion rate of these leads may be higher than that of generic SEO traffic. Admittedly, you may see fewer in volume at first, but each lead will likely be “warmer.” The key is to make the most of it with an excellent user experience (easy contact forms, quick demos, etc.).
GEO also offers an opportunity to strengthen your brand image. By shaping your content to be as useful, clear, and reliable as possible, you improve the perception of your business across all audiences: AIs, human readers, and existing clients who appreciate your educational resources.
This pursuit of quality can push you to become a thought leader in your sector, producing resources that everyone cites (including competitors). Ultimately, it’s a win-win: more visibility in AI-generated answers, and more respect from your professional community.
Finally, GEO forces you to innovate and stay informed about search engine evolution. In doing so, you build an internal culture of marketing agility. Search engines will evolve, AIs too—but if your team is used to adapting (e.g., by testing new tools to track presence in AI outputs or experimenting with innovative content formats), you’ll always stay one step ahead.
Consider GEO as a learning ground that will make you more competitive overall—even beyond AI, across all aspects of digital marketing.
Conclusion: GEO and SEO hand in hand toward the future of search
GEO is quickly moving from being a buzzword to becoming an essential skill for digital marketers. Don’t think of it as a radical break from SEO, but rather as its natural extension in a new technological context. Sure, tomorrow’s search engines won’t just display a list of blue links—they’ll deliver an AI-written response. However, to build that response, AIs will still need high-quality content produced by humans—that is, by you, your company, your writers.
By following the recommendations shared in this article, you’ll start adapting your content so it can seamlessly travel across formats and interfaces. Whether someone searches on Google or asks an open question to ChatGPT, your goal is for your expertise to surface at the right moment. GEO and SEO don’t cancel each other out—they complement one another. By investing in both, you ensure maximum visibility.
Remember, we are still at the beginning of this transition. GEO best practices will continue to evolve as we better understand how AIs select and present information. Stay curious, keep learning—read studies, test queries yourself on different platforms, follow feedback from other specialists. This adaptability will be your strongest ally.
In the meantime, it’s not too early to take action: audit your existing content, identify quick GEO wins (a FAQ page to structure, an expert article to update, a guest post to publish on an influential site…), and get moving. Every small step toward clearer, more reliable, and better-structured content is a step toward greater visibility in the generative AI landscape.
SEO has long been king, but a new era is opening with GEO. By intelligently combining both, you’ll be ready to dominate across all engines—whether they run on links or artificial intelligence.
Don’t wait for competitors to get ahead: the time is now to optimize for the next generation of leads!
For more on best practices for integrating AI into your business, check out our complete guide.